Catalogue - Key Takeaways Show
The Ethereum blockchain’s principal token, Ether (ETH), is the world’s second-largest crypto by market capitalization. Ether, like Bitcoin, is a cryptocurrency that may be used to transfer funds directly to another person without using an intermediary like a bank.
Ethereum’s long-term goal is to be used for more than simply financial transactions. On Ethereum, software developers can create applications ranging from decentralized lending platforms to social media networks.
The Ethereum blockchain requires all users to pay a gas price before carrying out any action.
Nothing goes for nothing, and that includes services and products. For example, using an ATM to withdraw $20 for $5 can be inconvenient. Just as sending $500 for $100 can be outrageous for the average user.
This can sometimes be the case for transmitting a transaction or performing a function on the Ethereum network, even though it seems extreme. And unlike ATM fees, the Ethereum network will not reimburse you for your gas fees by month-end.
What Gas means?
For a user to interact with the Ethereum network, the network requires a certain amount of ether (ETH), the native money of Ethereum. Ethereum miners employ these fees to cover the energy costs of transaction verification and to protect the Ethereum network from spammers by making it prohibitively expensive for them to do so.
Ethereum’s gas costs, while their effectiveness in encouraging miners to continue confirming transactions and maintaining network security are a source of incredible frustration for many users. Not only do people despise paying for Gas, but it can be prohibitively expensive if the network is crowded.
“Ethereum gas fees are like Uber surge prices. You have to be drunk not to notice how bad they are”– @pixiekate13
The computational effort required to carry out specified activities on the Ethereum network is measured in terms of Gas.
How are Gas fees calculated?

Fees for completing a transaction can be calculated in a variety of ways. For example, a sender might theoretically set their charge because of the network’s design, but this wouldn’t work because fees compensate miners.
Users can estimate how much Gas they’ll need for their transaction by using one of the many online gas calculators. However, the Ethereum Gas Station is famous for its accuracy and user-friendliness. Consider that proposed prices are simply estimates and can vary at any time.
Even without an internet calculator, you can figure out your transaction fees. For a sender, they would need to know how much Gas each Ethereum activity requires and the average gas price in the market.
Before the London upgrade
Ethereum transaction costs were recalculated in August 2021, when the London Upgrade occurred. A brief history of how things used to work is provided here:
Let’s assume Olivia owes Tom 1 ETH. The gas fee is set at 200 gwei, and 21,000 units limit.
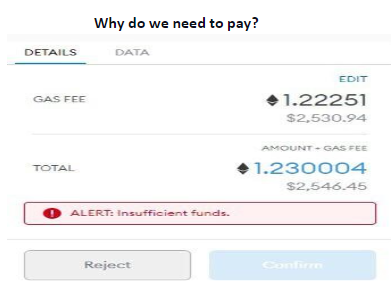
The cost would be Gas units (limit) X Gas price/unit. Which is 21,000 X 200 = 4,200,000 (0.0042 ETH).
Upon completing the transaction, 1.0042 ETH would be debited from Olivia’s account. This means Tom would get 1.0000 ETH, while the miner would get 0.0042 ETH.
After the London upgrade
Ethereum’s gas fees have been overhauled as part of the London Upgrade, which took effect on August 5, 2021. Better estimation of transaction fees, typically faster transaction inclusion, and offsetting ETH issuance by eliminating a percentage of transaction fees are just a few of the high-level improvements brought on by this modification.
This cost depends on the demand for space in a particular block, starting with London’s network upgrade, and is based on a minimum price per gas unit. As the transaction charge’s base cost is depleted, customers are expected to add a tip (also known as a priority fee) to their purchases. Most wallets are anticipated to automatically set the tip to compensate miners for executing and spreading user transactions in blocks.
The total transaction charge is calculated as follows: (Base fee + Tip) X (Gas units)
Assume Nicholas is required to pay William 1 ETH. The transaction has a gas limit of 21,000 units and a base charge of 100 gwei. Nicholas includes a 10-gwei tip.
Using the method above, this equals 21,000 X (100 + 10) = 2,310,000 gwei, or 0.00231 ETH.
Nicholas’ account will be debited 1.00231 ETH when he sends the money. William will receive a credit of 1.0000 ETH. Miner receives a 0.00021 ETH tip. A charge of 0.0021 ETH is burned as the base fee.
Nicholas can also specify a maximum gas (max gas fee) for the transaction. That way, he receives a refund equal to the difference between the full fee and the actual fee, meaning refund = max fee — (base fee + priority fee). When he selects a maximum gas fee for the transaction, he doesn’t have to worry about going “over” the base charge when the transaction is completed.
Ethereum users pay gas fees to cover the cost of processing and approving transactions on the blockchain. The ‘fuel’ limit is the maximum amount of Gas (or energy) you’re willing to spend on a given transaction.
To complete a transaction utilizing ETH or a smart contract, you’ll need to put in more effort.
For example, the cost to run a real-world car for X miles may take Y gallons of fuel, just as the cost of transferring X dollars from your bank account to another’s account or credit card may cost you Y dollars in fees. In all scenarios, X represents the value of the vehicle trip or financial transaction, whereas Y represents the activity’s cost.
This is similar to a contract or transaction on Ethereum, which may be valued at 50 ETH (X), and the gas price to complete this transaction at that period might be 1/100,000 (Y).
This fee is paid to the Ethereum miners who conduct all of the crucial responsibilities of validating and executing transactions on the network. Miners can disregard such transactions if the gas price cap is set too low. So the price of gas changes (priced in ETH) depending on the amount of processing power available.
Why cost so much?
We can better comprehend why gas fees are so high since we understand how total gas fees are determined. There are two main reasons why gas fees are relatively high:
– The denomination of gas fees in gwei.
– The variable total fee formula used by Ethereum.
Higher ETH price means higher gas prices.
The fact that ETH is more expensive is the primary cause of the rise in gas fees. Recall that gas fees are charged in gwei, a new way of expressing the value of an Ethereum (Eth) token. In addition, decentralized finance (Defi) and non-fungible tokens (NFT) are two key reasons why the demand for Ethereum is rising.
Gas fees are higher because base fees are higher
Furthermore, gas fees have skyrocketed because Ethereum’s charge formula constantly changes. Base fees are the least amount of Gas needed to include a transaction on the Ethereum blockchain, and they are adjusted based on demand for transaction inclusion. As a result, the Ethereum blockchain’s base fees have steadily risen over time.
According to State of the DApps, over 3,000 decentralized applications (dApps) are currently running on the Ethereum blockchain. All of them are hoping to have their operations included alongside those of other Ethereum network users. Dapps alone makeup up over 100,000 daily active users on Ethereum, processing over 700,000 transactions every day.
In another way, Ethereum’s broad use has resulted in higher base costs and a significantly more variable supply of Gas for base fees. Ethereum’s EIP 1559 upgrade changed the computation of base fees to be decided by the transaction preceding it to make gas fees more uniform. However, due to the rising demand for Ethereum, the total cost of gas fees has risen due to EIP 1559’s base fees.
The switch to proof-of-stake (PoS) from proof-of-work (PoW) as the standard for Ethereum’s consensus algorithm is part of Ethereum 2.0, a significant upgrade to the Ethereum network. The upgrade promises to lower Ethereum fees in line with other market competitors by considerably boosting transaction-processing capabilities and eliminating miners from the equation.
Any relations to the growing DeFi NFT market?
Digital investors and sellers are embracing NFTs at an ever-increasing rate. Everyone hurriedly acquires various uncommon NFTs to store as digital valuables in their wallets and hard drives. However, when it comes to collectors and sellers alike, you’re well aware of the significant transaction costs that must be borne. These are known as “crypto Gas fees.” They are increasing rapidly in tandem with the popularity of decentralized financing (DeFi).
Since the Ethereum blockchain is the most widely used, many DeFi-based NFTs rely on it. As a result, the Ethereum blockchain becomes jammed and overcrowded. Furthermore, since it can only process 30 transactions per second, it depends upon the proof of work mechanism to verify large-scale transactions.
Transactions that need the payment of gas charges:
The cost of Gas is incurred at each stage of the journey. So even if you go on to add cash to your wallet or convert ETH to WETH, you’ll still have to pay the gas expenses.
The following transactions necessitate the payment of gas expenses.
- Developing an NFT: To create an NFT, you’ll need to create a digital asset called an NFT token on the blockchain. As part of creating an NFT token on the blockchain, blocks containing data related to the smart contract and other metadata are added to the blockchain. For the blockchain network to function, gas charges will be incurred.
- Selling an NFT: Most NFT markets do not charge fees for advertising an NFT for sale. However, some do charge service fees immediately. In addition to the gas fees needed to complete the transaction, some charge this fee when the NFT is sold.
The term “Lazy minting” refers to the same concept. - Buying an NFT: Everyone is affected by the high cost of Gas, not just retailers. If you place an order for an NFT or even cancel one, you must pay the gas fees. Likewise, to send the crypto from your wallet to the seller’s wallet, you must pay a gas cost when the deal is complete.
The effects of “Gas” on Artists
The introduction of Gas has significantly impacted NFT art and artists. When gas prices are high, aspiring artists cannot make, mint, or even purchase other works. As a result, some artists try to incorporate the cost of gasoline into their work.
As a result, collectors are forced to choose between spending 25–57% of the total purchase price on gasoline and the perceived “value” of their work. This is a problem for artists who want to establish a following.
In some circumstances, the cost of gasoline has exceeded the price of creating a work of art, making it unsustainable for an artist even to post their job online.
What will be the future of this?
Ethereum’s unpredictable and occasionally exorbitant gas charge has been one of the leading causes affecting ETH users and the entire community of crypto investors. Critics have mentioned this issue as one of Ethereum’s most deadly vulnerabilities, providing several opportunities for ‘Ethereum murderers.’ Nonetheless, ETH remains one of the market’s most popular cryptocurrencies, second only to Bitcoin.
There are no free transactions in the sector, and investors know this. However, the Ethereum gas fee irked many investors. Furthermore, blockchain technology’s motto of inclusiveness is undermined by the requirement to pay a hefty transaction fee only to complete a single transaction. Some consumers may not be able to afford to pay these high costs.
Investors were concerned about Ethereum’s gas fee mechanisms because they believed that the cryptocurrency would lose its relevance if better alternatives became available.
In the proof-of-work blockchain, gas fees have become standard, but for Ethereum, they have started to drive developers and users away from Ethereum. Because other cryptocurrencies offer speedier transactions with cheaper costs, many experts expected that the gas fee would remain high until a switch to a proof-of-stake consensus method was made.
They have since become some of Ethereum’s strongest rivals. However, ETH owners should not be concerned about the cryptocurrency’s dwindling market share.
Several Ethereum users have found this reduction in gas fees a boon. Slighter arbitrage possibilities and improved capital efficiency are now possible since network transactions are now less expensive. In any case, they need to be aware of the forthcoming situations in the crypto market, which they should. At this time, the volatility of cryptocurrencies is at its highest point. Because of this, investors should take their time before making any hasty decisions.
Will Ethereum Gas Prices Change After The Upcoming Merge?
As the Ethereum merge date draws closer, investors and traders are wondering just how the event will shake up Ethereum Gas Prices.
Now with the merge being scheduled for the middle of next month, crypto investors are hoping that Ethereum’s transition to PoS may bring some reprieve from high gas fee charges.
However, in a recent update, The Ethereum Foundation has finally shared an update adding that the gas fee prices will remain unchanged even after the merge. Instead, ETH gas fees may fall when Ethereum gets to the next phase after the merge — sharding, which is set to launch in 2023.
In addition, transactions will also not be noticeably faster after the Merge. However, post-merge APR yields on the network are expected to increase by 50% compared to now to attract capital.
Ethereum DanKsharding
Ethereum gas prices have relatively remained the same after the Shanghai Upgrade in April 2023. Whereas, an average of 25 Gwei in late March to 113 Gwei in start of May is seen. Moreover, Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP 4844) danksharding in late half of 2023 would ease the gas fee for developers. In short, danksharding will provide vast quantities of space on the Ethereum blockchain for rollups to dump their compressed transaction data, reducing the cost of rollup execution.
About Coinflare
Coinflare is a cryptocurrency exchange platform that offers traders a secure, easy-to-use, and convenient way to buy, sell and trade cryptocurrencies. Our platform has been designed with investors of all levels in mind, whether they are just starting out or experienced traders. We offer various features and tools to help users make the best trading decisions possible, including advanced charting and analytics, real-time market data, and various customisable trading interfaces. At Coinflare, we are dedicated to empowering our users and helping them reach their financial goals.
Stay in the loop about our launches, trading pair announcements, contests and more by following u on Discord, Telegram, and Twitter.








